An object positioned in space may be imagined as surrounded by six mutually perpendicular planes. So, for any object, six different views may be obtained by viewing at it along the six directions, normal to these planes. Figure 3.5 shows an object with six possible directions to obtain the different views which are designated as follows:
1. View in the direction a = view from the front
2. View in the direction b = view from above
3. View in the direction c = view from the left
4. View in the direction d = view from the right
5. View in the direction e = view from below
6. View in the direction f = view from the rear
Figure 3.6a shows the relative positions of the above six views in the first angle projection and Fig.3.6b, the
distinguishing symbol of this method of projection. Figure 3.7 a shows the relative position of the views in the third angle projection and Fig. 3.7b, the distinguishing symbol of this method of projection.
NOTE A comparison of Figs. 3.6 and 3.7 reveals that in both the methods of projection, the views are identical in shape and detail. Only their location with respect to the view from the front is different.
MACHINE DRAWING
Third Edition
Dr.K.I. Narayana
Dr.P. Kannalah
K. Venkata Reddy
NEW AGE INTERNATIONAL (P) LIMITED, PUBLISHERS
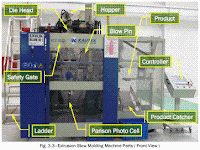
Extrusion Blow Molding Machine Parts and Functions
Extrusion Blow Molding Machine Parts and Functions
• Extruder Motor—Drives the screw in the barrel to rotate and push the
melted material into the die head.
• Gearbox—Reduces the speed of the extruder motor into a required speed enough to push the material into the die head.
• Hopper—A feed reservoir into which the material is loaded.
• Extruder—A part of the machine that accepts solid resin material, conveys it in a surrounding barrel by means of a rotating screw, melts the
material by means of heaters, and pumps it under pressure into the die
head.
• Cooling Fans—Cools down the barrel during machine shut down to prevent the material from degradation.
• Heating Bands—Device attached on the barrel and the die head used to melt the solid material at a required set temperature.
• Die Head—Used to form the melted resin into a parison and also used for adjusting the characteristics of molten resin to create a stable parison.
• Die & Pin—Used to align the flow of parison to get a good and centered parison.
• Hot Cutter—Cuts the parison after the mold is closed for the blowing process.
• Blow Pin—Used to blow compressed air into the parison to inflate it after the mold has been closed and form the desired design of the mold.
• Mold—A hollow form or a cavity into which a molten plastic material, called parison, is introduced to give the shape of the required component.
• Deflasher—Used to cut the excess material on the bottle which is called a flash material (top and bottom).
• Post Cooling—A part of the machine that is used to cool down the inside of the bottle, to lessen the cooling time required inside the mold.
• Article Discharge—A part of the machine used to take the bottle out.
Higher Institute for Plastics Fabrication
WORKBOOK
for
Extrusion Blow Molding
Practical Course
Prepared by
Extrusion Blow Molding Department
1st Edition 2009
What Is Computer-Aided Process Planning (CAPP)?
In this section we introduce the topic of CAPP, and review important components of this technology. Chang and Wysk (1985) define process planning as “machining processes and parameters that are to be used to convert (machine) a workpiece from its initial form to a final form predetermined from an engineering drawing.” Implicit in their definition is the selection of machining resources (machine and cutting tools), the specification of setups and fixturing, and the generation of operation
sequences and numerical control (NC) code. Traditionally, the task of process planning is performed by a human process planner with acquired expertise in machining practices who determines from a part’s engineering drawings what the machining requirements are.
Manual process planning has many drawbacks. In particular, it is a slow, repetitive task that is prone to error. With industry’s emphasis on automation for improved productivity and quality, computerized CAD and computer-aided manufacturing (CAM) systems which generate the data for driving computer numerical control (CNC) machine tools, are the state-of-the-art. Manual process planning in this context is a bottleneck to the information flow between design and manufacturing.
CAPP is the use of computerized software and hardware systems for automating the process planning task. The objective is to increase productivity and quality by improving the speed and accuracy of process planning through automation of as many manual tasks as possible. CAPP will increase automation and promote integration among the following tasks:
1. Recognition of machining features and the construction of their associated machining volumes from a geometric CAD model of the part and workpiece
2. Mapping machining volumes to machining operations
3. Assigning operations to cutting tools
4. Determining setups and fixturing
5. Selecting suitable machine tools
6. Generating cost-effective machining sequences
7. Determining the machining parameters for each operation
8. Generating cutter location data and finally NC machine code
Traditionally, CAPP has been approached in two ways. These two approaches are variant process planning and generative process planning. In the following section we discuss these and other issues in a review of work in this field.
THE
MECHANICAL
SYSTEMS
DESIGN
HANDBOOK
Modeling, Measurement,
and Control
OSITA D. I. NWOKAH
YILDIRIM HURMUZLU
Southern Methodist University
Dallas, Texas
CRC PRESS
Boca Raton London New York Washington, D.C.
Polymer molding
Thermoplastics are molded as viscous liquids. Injection molding and extrusion dominate, but all molding processes impose flow that can orientate the molecules; if the molding is cooled fast enough the alignment is frozen in (Figure 19.5).
If not, polymers mostly prefer to form an amorphous structure. In some polymers crystallinity may develop on slow cooling. All polymers shrink as the mold cools from the molding temperature to room temperature because of thermal contraction and the loss of free volume caused by crystallization. Allowance must be made for this when the mold is designed.
Materials
Engineering, Science,
Processing and Design
Michael Ashby, Hugh Shercliff and David Cebon
University of Cambridge,
UK
AMSTERDAM • BOSTON • HEIDELBERG • LONDON • NEW YORK • OXFORD
PARIS • SAN DIEGO • SAN FRANCISCO • SINGAPORE • SYDNEY • TOKYO
Butterworth-Heinemann is an imprint of Elsevier
Labels
2d
(1)
3D
(1)
ABG
(1)
agen JNE
(1)
almari
(1)
Alufoil
(1)
Aluminum Foil
(1)
anilox roll
(1)
apartemen
(1)
Atom
(1)
autocad
(1)
backdrop logo
(1)
bagian dalam
(1)
bangunan
(1)
batu alam
(1)
berkualitas
(1)
bermutu
(1)
berpengalaman
(1)
bertingkat
(1)
birdview
(1)
black and white
(1)
botol plastik
(1)
cafe
(1)
classic
(1)
coklat
(1)
cold rolled sheet
(1)
Computer To Plate
(1)
Consumer Understanding
(1)
control movement
(1)
counter
(1)
CTP
(1)
denah berwarna
(1)
denah kantor
(1)
desain
(1)
desain cuci mobil
(1)
desain kamar
(1)
desain produk
(1)
design
(1)
Design and Function
(1)
design meja
(1)
Design restaurant
(1)
design rumah
(1)
di daerah
(1)
dinding bata
(1)
dining
(1)
Duromer
(1)
Electrons
(1)
etnik
(1)
factors
(1)
flexo packaging
(1)
flexo printing
(1)
food
(1)
furniture
(1)
gallus
(1)
gambar
(1)
gaya modern
(1)
gloss
(1)
grc kotak
(1)
Halftone
(1)
hanya 550 ribu
(1)
harga murah
(1)
hasil cepat
(1)
hotel
(1)
industrial
(1)
injection
(1)
Injection Mold
(1)
ink
(1)
inovatif
(1)
install
(1)
interior
(1)
interior rumah
(1)
jasa gambar rumah
(1)
jasa 3d
(1)
jasa arsitek
(1)
jasa desain
(1)
jasa desain 3d
(1)
jasa design
(1)
jasa designer
(1)
jasa gambar
(1)
kamar tidur
(1)
kamar tidur anak
(1)
kampus
(1)
karaoke
(1)
kawasan
(1)
kawasan industri
(1)
kemasan
(1)
kerja di rumah
(1)
kitchen set
(1)
kontemporer
(1)
kosan
(1)
kost
(1)
krem
(1)
laci
(1)
lamination
(1)
lithography
(1)
living room
(1)
livingroom
(1)
lounge
(1)
Luscher MultiDX
(1)
masterplan
(1)
matt
(1)
meja kerja
(1)
metalworking
(1)
mewah
(1)
minimalis
(1)
minimalist
(1)
modern
(1)
mold
(1)
molding
(1)
Monomer
(1)
murah
(1)
murah.
(1)
Neutron
(1)
nuansa remaja
(1)
offset
(1)
online design
(1)
open ceiling
(1)
outdoor
(1)
overprint
(1)
pabrik
(1)
pantai
(1)
pencahayaan
(1)
perumahan
(1)
pesan desain
(1)
pesan desain toko
(1)
plug
(1)
Polimer
(1)
Polyaddition
(1)
Polycondensation
(1)
Polymerization
(1)
Polystyrene
(1)
printing ink
(1)
Product Creation
(1)
product function
(1)
produk katalog
(1)
Protons
(1)
Raster Image Processor
(1)
register
(1)
rendering
(1)
resepsionis
(1)
responsibility
(1)
resto industrial
(1)
RIP
(1)
Rotary
(1)
ruang kantor
(1)
ruang keluarga
(1)
ruang kerja
(1)
ruang tamu
(1)
ruang tunggu
(1)
ruko
(1)
rumah
(1)
rumah hook
(1)
rumah susun
(1)
rumah tropis
(1)
scandinavian
(1)
screen printing
(1)
sederhana
(1)
sempoa
(1)
setup
(1)
simple sederhana
(1)
specifications
(1)
spring
(1)
steel
(1)
Struktur Plastik
(1)
suspension
(1)
sweet home
(1)
taman
(1)
tampak
(1)
tampak rumah
(1)
Technological Change
(1)
terbaru
(1)
termurah
(1)
toko aksesoris
(1)
toko asesoris
(1)
trapping
(1)
two cavity
(1)
unscrewing
(1)
use
(1)
uv varnish
(1)
via online
(1)
website
(1)