Struktur Plastik Monomer Polimer Duromer
NEW PRODUCT CREATION
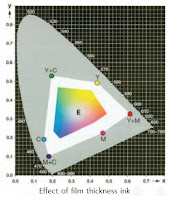
Color Reproduction in Printing
Raster Image Processor RIP Express
Design Definition and Design Technology
Injection Mold for the Body of a Tape Cassette
Learn Flexo Packaging Register Overprint Trapping
Polymer Structure Polymerization Polycondensation Polyaddition
Polymer means many mers or units, generally a repetition of hundreds or thousands of times a chain-like structure. Most monomers are organic materials in which the carbon atoms are joined in covalent bonds with other atoms, such as hydrogen, oxygen, nitrogen, fluorine, chlorine, silicon and sulfur.
To form macromolecular bonds from each thermoplastic material molecule is done in three ways, namely:
a. Polymerization:
Bringing together several similar molecules to form a large molecule Polymerisate. The monomers in polymers can be linked in repeating units that lengthen and enlarge the molecules by a chemical reaction known as a polymerization reaction. Despite the many variations, the two basic processes are Condentation polymer and Polyaddition.
b. Polycondensation;
The bonding of several molecules to form large macromolecules through the process of separating one of the atoms to bind small molecules from water. From this process, a material called Polycondensate is formed
c. Polyaddition;
Namely the union of several basic molecules through the placement of several molecules without separation of the non-fixed parts. The material formed is called "Polyadducf. In this reaction an initiator is added to break the two bonds between the carbon atoms and start the bonding process by adding more monomers to build the chain. For example the Ethylene monomer bonds to produce a polymer known as Polyethylene .
The sum of the molecular weights of the mer-mers in the polymer chain is the molecular weight of the polymer. The higher the molecular weight in a given polymer, the greater the chain length. Since polymerization is a random event, the resulting polymer chains are not all the same length, but the resulting chain lengths are formed in a traditional distribution curve. We determine and express the average molecular weight of a polymer on a statistical basis by averaging. The distribution of the molecular weight distribution is referred to as the molecular weight distribution (MWD). Molecular weight and MWD have a strong influence on polymer properties. For example, fracture and impact strength, resistance to cracking, and viscosity in the liquid state all increase with increasing molecular weight. Most of the polymers traded have molecular weights between 10,000 and 10,000,000.
In some cases, it is easier to describe the size of a polymer chain in Degrees of Polymerization (DP), defined as the ratio of the molecular weight of the polymer to the molecular weight of the repeating unit. For example, Polyvinyl chloride ( PVC) has a mer weight of 62.5, so the DP of PVC which has a molecular weight of 50,000 will be 50,000 / 62.5 = 800. In the polymerization process, the higher the DP, the greater the polymer viscosity, or flow resistance, thus making it easier to formation and overall costs.
During polymerization the monomers are bonded together in a covalent bond, forming a polymer chain. Because of their strength, covalent bonds are also called primary bonds. In addition, polymer chains hold on to secondary bonds such as van der Waals bonds, hydrogen bonds and ionic bonds. Secondary bonds are weaker than primary bonds. In a polymer, the increase in strength and viscosity with molecular weight is partly due to the fact that the longer the polymer chain, the greater the energy required for secondary bonding.
If the repeating units of the polymer chain are of the same type, we call the molecule a homopolymer. However, two or three types of heavy monomers can be combined to obtain special characteristic advantages, such as improved strength and durability. Copolymer consists of two types of polymers such as Styrene-butadine, widely used for car tires. Terpolymer consists of three types such as ABS used for helmets, telephones.
Rotary screen printing an effective way of printing
Desain Tempat Usaha Cuci Mobil dan Toko Asesoris
Two-Cavity Unscrewing Mold for a Glass Fiber Reinforced Polyamide Threaded Plug
DESIGN PRODUK KEMASAN BOTOL PLASTIK
LAMINATION and UV VARNISH
Computer to Plate versus Computer to Film
INJECTION MOLDING PROCESS
Easy Way and Quickly Draw With AutoCAD
Atom Electrons Protons Neutron
Factors Affecting Product Design
Product design is a tool in production management starting from previous research and development.
Doing product design is not just a decoration of the product, but whether the design is able to influence our products will be accepted or not by consumers.
The importance of product design lies in determining in detail the design of the product to be made, as well as the classification so that it fits the desired objectives.
Factors that influence Product Design include:
-Product function
Each product that will be produced has a different function or use, this depends on what purposes the product is made for. Thus that product design is related to the form and function of a product. Both play an important role in determining a product design which is basically to provide maximum satisfaction for consumers or customers both in terms of quality and quantity.
-Design Standards and Specifications
In terms of specifications and design standards of a product, it will be seen from how to join the parts so that when they are put together into a strong unit
When designing the shape it is necessary to pay attention to beauty by adjusting the design according to its function and use.
Plan a balanced size of product parts as a whole.
The quality of a product must be adjusted according to the function of the product, if it is to be used for a long time, then the quality of the product must be high when compared to the product that will be used in a short period of time.
If the product to be used wants to have good quality, then the materials used must also be able to support everything that is expected to be realized and the customer feels their own satisfaction.
Color has its own meaning for consumers, because each person has a unique characteristic and preference for certain colors. And this is what the company must pay attention to in order to compete with other similar companies.
-Product responsibility
This is one of the responsibilities of the producer as a product maker to consumers for the safety and comfort of the product's user. Therefore this factor is very important to be considered by the company when designing the product.
-Price and Volume
Prices are associated with the number of products to be made, for products to be made based on orders, usually the selling price will be different from products made to be distributed to broad consumers, whose prices are relatively cheaper so that the product design will be different.
-Prototype
Prototype is the first product model to be made, this prototype shows the actual form and function, so that before the company produces the prototype is made an effort to make first.
From the prototype testing, if it passes the test it may provide an overview of the changes that need to be made as well as information in the final preparation of the product design.
-Factors of the Beauty of Product Design
If the packaging is beautiful and can attract the attention of consumers, consumers will be interested in buying it. For example, the marketing strategy for food products, this part of the industry is very important for displaying packaging images that can arouse appetites for consumers who see it.