Steel is a compound of iron (Fe) and Carbon (C), which often also added the element chromium (Cr), Nickel (Ni), Vanadium (V), Molybdaen (Mo) and others to get certain properties desired on the application in the field, such as anti-corrosion properties, heat resistance, high temperature resistant.
Compared to other types of metals (eg Aluminium, Copper, etc.) then the iron / steel is the material most widely produced in the world today. Statistics show that 92% of the world is the use of metallic iron / steel. In 1998, production Rohstahl / raw steel (raw steel) amounting to 750 million tonnes. Because of the large market share of this steel, the advanced countries in the steel industry are competing to create a new engineering-engineering in the production process. The goal is to get good quality steel with a relatively cheap price.
One of the important intermediate product is steel plate (strip, plate, sheet) with a wide variety of thicknesses. Steel plates are widely used as a raw material for production of car body of a car, train, to kitchen utensils.
Conventional process of manufacturing steel plates are usually as follows: The first time, liquid steel cast by the method Strangguss / continuous casting. From here the obtained results in the form of steel bars (slabs) with a thickness of 150 to 320 mm. The next process is the thinning of the thickness with a rolling mill in order to obtain a thin slab 2 to 20 mm. One way of simplification of production is to create a continuous casting installation capable of producing steel with a thickness below 150-320 mm. Since 1980, has successfully cast steel bar with a thickness below 25 mm (eg CPR method). Thus could be savings in the process of rolling.
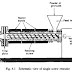
Since these fifteen years the Institute for metal forming (IBF), RWTH Aachen University of Technology, Germany in cooperation with Thyssen Krupp Stahl AG (TKS) tried to do a new breakthrough in the production of strips (thin steel plates). This new breakthrough has actually only dream of long ago by Sir Henry Bessemer in 1891. Experts from the British steel has even patented the design and installation of thin steel-making process known as "double-roller process." In this principle, liquid steel cast in between two rollers (cylinders) water-cooled, rotating in opposite directions. The thickness of steel plates produced depends on setting a gap between the two cylinders. Another factor affecting the geometry of the product is spread pressure (pressure) between the slit and also the spread of temperature in the cylinder. The next stage, steel plates passed on cooling (water), then through the cold rolling, and finally rolled up (coiling). With this method, have been successfully cast in steel plates with thickness below 3-4 mm, so only with the process of rolling one step can be obtained steel with thickness as the finished product. The principle of this new double-roller process can be realized in the late 20th century along with the progress of computerization in the field of control and measurement technology.
In this world, according to one researcher from TKS AG, this method was developed in Italy, Australia, Japan, and Germany. While the USA would prefer to buy the works from Australia. Until now, each competing with each other, and each other to hide the results have been achieved. TKS AG itself has created an installation in thin strip casting (casting thin steel plates) with a double roller method in one of its factories in the town of Krefeld, Germany. On December 10, 1999 has done a test installation first time, with the result of thick steel plates 3 mm, width 1100 mm, weight 36 ton. The material is cast steel of the type of stainless-steel. Later, Krefeld will produce strip with a thickness of 1.5 to 4.5 mm, width 1050 up to 1350 mm, with a speed of 100 meters per minute
Industrial product design
In line with the progress of industrialization, a product is required not only has economical and technical functions merely the fulfillment of physical needs, but also to answer the demand for a symbolic function, beauty, comfort, and convenience. The problem that then arises is why there are products that are superior to other products, while the specifications are almost the same. Above phenomenon causes a demand for industrial designs that can meet the real needs of consumers in the competitive market.
Industrial product design is an extensive activity in technological innovation. The moves include product design product development process by considering the functionality, usability, production processes and technologies, marketing and improvements to benefits and aesthetics of industrial products.
To improve competitiveness, quality and productivity, needed a research activity and development of new products. It is anticipated by the industrial product design education. Judging from the type of activities, the scope of the profession is divided into three major groups:
1. Design products include:
Furniture, household equipment, electronics, medical and hospital equipment, office supplies, building components, sports equipment and hobbies, crafts, etc..
2. Design of environmental facilities include:
Sports and recreation facilities, urban information systems, tools and utilities of the city, shelter and means of foot-five, farming equipment, farming and forestry, etc.
3. The design of transportation include:
Passenger cars, family cars, buses, public transport, trucks, transport of goods, interior share the type of transportation equipment, firefighters, airport buses, garbage units, transport facilities and other environments.
Studies of industrial product design is one of support for an industrial engineering degree. In the process of planning and production control, industrial engineering graduates is expected to formulate a concept of some form of integrated production systems in terms of product design, tools, and functions, as described above. In this case, an IT graduate is expected to interact with scholars from other fields to achieve a tangible result.
A designer of industrial products are expected to possess and develop the characteristics of creative, original, and have the ability in processing the form, capable of working together in multidisciplinary, familiar environment and cultural characteristics, controls applied in the field of ergonomics and marketing, and able mempresntasikan ideas systematically and clearly.
Currently, in industrialized countries, the profession of industrial design is one of the chain backbone in the industry working hand in hand with the engineers, architects, economists, ergonom, material experts, scientists, even with the artists to deliver a specific requirement. In other words, a product designer is a figure that bridges the interests of producers and consumers. In Indonesia alone is estimated to total production designer is still limited. In addition, the expected contribution is still not evident, given that most of our industry is still making raw materials.
But in the future of this profession is expected to contribute significantly to the sustainability of industry in Indonesia, so as to produce comparative and competitive advantage in the like product. Activities at the stage of product design R & D / product development to define industrial products. This activity is the key, the concept and developed the product strategy. Industrialized countries will not release these activities, in addition to business networking and marketing are also retained.
Injection Molding PROCESS
Use of goods made of plastic from time to time shows rapid growth, widespread almost all sectors of human life such as the use for: equipment and household goods including clothing and equipment for cosmetics, equipment and office supplies, facilities in education, building , transformation, electrical and electronic equipment, automotive, aircraft, agriculture and fisheries sector and many other uses.
This is because plastic has the ability to substitute materials made from wood, metals, rubber, leather, glass and others.
Along premises developments use plastic, plastic industry and the development of processing facilities has grown rapidly plastikpun.
In the processing of plastic into a plastic goods known to have some type of plastic processing machines like: thermoforming, Extrusion, blowmolding, injection molding, tubes and more. From a group of plastic processing machines may be grouped based on the work process that is continually working engine and machine work cycle, including injection molding machine that processes at work in cycles.
Injection molding machine has the function to change the plastic material of the form of granules [plastic seed] or puder into plastic goods that have a shape.
Of the many plastic products represents nearly 80% of plastic products.
The process is a plastic material in the form of granules or puder was heated to be melted, then injected with the aid of screw drive plunger into the hollow mold and cooled, then frozen plastic Limer. Hardened and shaped according to the shape of the cavity, the last product released.
Step-by-step process is called a cycle, ie the process step to the original will always be repeated when the one-step operation is completed.
The quality of the results of the process [product] will depend on engine operating conditions, the quality of processed materials mold / molds and conditions of the machine itself, where the condition of the engine would be better if all the components or parts of machinery and mold works well and balanced.
Process injection molding machine
a) Matter is closed and restrained, the material has been injected into the mold / mold.
b) Screw moved back, a replacement of down and get into the cylinder and collected in the space in front of the cylinder.
c) The result of the process (product) in the remove from the mold / molds.
The Bending Process
INTENT The intents of this part of the tutorial are to discuss some basic mechanical concepts used in describing bending of sheet metal and to introduce a limiting condition on the amount of deformation that can be imposed in bending. A superficial summary is
- how can deformation be described?
- what is the minimum bend radius that can be produced?
Introduction
Bending is one of the most common metalworking operations. Parts are made by bending of sheet stock and bending also is a component of more complex sheet metal forming operatins. Bending is the plastic deformation of metals about a linear axis called the bending axis with little or no change in the surface area. When multiple bends are made simultaneously using a die, the process is sometimes called forming. What distinguishes bending is that the bend axes are linear and independent. Independence means that bending about one axis has no effect on the bending about the other axis. For example, a blank with four separate tags along the edges of a rectangular section can be bent into a box by bending each tab separately. In contrast, forming a box or rectangular pan from a rectangular sheet by using a punch and die is called a drawing operation. The corners of the pan are formed simultaneously and the deformation around a corner is determined by both edges and how they interact at the corner. If the axes of deformation are not linear or are not independent, the process becomes drawing and/or stretching, not bending.
The bending process is used not only to form parts such as angle sections, flanges, seams, and corrugations, but also to impart stiffness to the part by increasing its moment of inertia. Often changes in cross section shape can lead to increasing section stiffness without the addition of material.
The major concerns in bending are springback, the minimum length of workpiece needed to form a complex shape, the minimum bend radius possible the forces required. In this tutorial, we first present an overview of the deformation imposed in bending with an example of the shifting of neutral axis and its effects on bent part dimensions. We then define the strain imposed in bending since this quantity is needed to describe the details of the process. With a definition of strain and a material failure condition we can determine the minimum bend radius. Finally, the problem of springback in bending is discussed and strategies to compensate for springback are presented.
Deformation in the Bending Process
In shearing a part of the blank is held and force applied to the other part of the blank. We can imagine that if the clearance is increased sufficiently, the result will be plastic deformation of the metals rather than material shearing and fracture. The figure at the right illustrates the forces applied during bending in V-dies, wiping dies, and U-dies. We can also imagine that when the tooling is retracted from the bent workpiece some elastic recovery or springback will occur. The final part shape will not be the shape of the blank as it is held in the die. The obvious solution to this springback problem is to overbend the workpiece. The amount of overbend is the real question and a process model which can predict this is useful.
The tooling used in bending operations results in the metal being deformed in localized areas only. The localized stresses occur only in the bend radius. The remaining flat part of the blank is not stressed during bending. The stresses acting in bending are illustrated in the following figures. The metal on the outside of the bend radius is stretched or elongated. The metal on the inside is compressed. If blank fracturing occurs during bending, it will occur at the outside bend surface. A process model which decribes strain in the bent region and a failure criterion can be used to predict the minimum bend radius (maximum strain) which can be produced. Any wrinkling will occur on the inside surface of the bend. This wrinkling also has to be taken into account when designing parts and processes but is usually less of a concern than is outside bend fracture.
During bending, one area of the blank is usually held stationary by a pressure plate called a pad. A local region of the blank is bent and the free blank areas move up or down to create the change in contour. This free metal movement is often called swinging and is a characteristic common only to bending operations. In design of a bending die, the swinging action must be predicted so that no obstacles are placed in the way. Because of this metal movement, the larger area of the blank is usually held stationary and the smaller blank area is alloowed to move.
(fr Jun Du and Barney E. Klamecki)
- how can deformation be described?
- what is the minimum bend radius that can be produced?
Introduction
Bending is one of the most common metalworking operations. Parts are made by bending of sheet stock and bending also is a component of more complex sheet metal forming operatins. Bending is the plastic deformation of metals about a linear axis called the bending axis with little or no change in the surface area. When multiple bends are made simultaneously using a die, the process is sometimes called forming. What distinguishes bending is that the bend axes are linear and independent. Independence means that bending about one axis has no effect on the bending about the other axis. For example, a blank with four separate tags along the edges of a rectangular section can be bent into a box by bending each tab separately. In contrast, forming a box or rectangular pan from a rectangular sheet by using a punch and die is called a drawing operation. The corners of the pan are formed simultaneously and the deformation around a corner is determined by both edges and how they interact at the corner. If the axes of deformation are not linear or are not independent, the process becomes drawing and/or stretching, not bending.
The bending process is used not only to form parts such as angle sections, flanges, seams, and corrugations, but also to impart stiffness to the part by increasing its moment of inertia. Often changes in cross section shape can lead to increasing section stiffness without the addition of material.
The major concerns in bending are springback, the minimum length of workpiece needed to form a complex shape, the minimum bend radius possible the forces required. In this tutorial, we first present an overview of the deformation imposed in bending with an example of the shifting of neutral axis and its effects on bent part dimensions. We then define the strain imposed in bending since this quantity is needed to describe the details of the process. With a definition of strain and a material failure condition we can determine the minimum bend radius. Finally, the problem of springback in bending is discussed and strategies to compensate for springback are presented.
Deformation in the Bending Process
In shearing a part of the blank is held and force applied to the other part of the blank. We can imagine that if the clearance is increased sufficiently, the result will be plastic deformation of the metals rather than material shearing and fracture. The figure at the right illustrates the forces applied during bending in V-dies, wiping dies, and U-dies. We can also imagine that when the tooling is retracted from the bent workpiece some elastic recovery or springback will occur. The final part shape will not be the shape of the blank as it is held in the die. The obvious solution to this springback problem is to overbend the workpiece. The amount of overbend is the real question and a process model which can predict this is useful.
The tooling used in bending operations results in the metal being deformed in localized areas only. The localized stresses occur only in the bend radius. The remaining flat part of the blank is not stressed during bending. The stresses acting in bending are illustrated in the following figures. The metal on the outside of the bend radius is stretched or elongated. The metal on the inside is compressed. If blank fracturing occurs during bending, it will occur at the outside bend surface. A process model which decribes strain in the bent region and a failure criterion can be used to predict the minimum bend radius (maximum strain) which can be produced. Any wrinkling will occur on the inside surface of the bend. This wrinkling also has to be taken into account when designing parts and processes but is usually less of a concern than is outside bend fracture.
During bending, one area of the blank is usually held stationary by a pressure plate called a pad. A local region of the blank is bent and the free blank areas move up or down to create the change in contour. This free metal movement is often called swinging and is a characteristic common only to bending operations. In design of a bending die, the swinging action must be predicted so that no obstacles are placed in the way. Because of this metal movement, the larger area of the blank is usually held stationary and the smaller blank area is alloowed to move.
(fr Jun Du and Barney E. Klamecki)
Labels
2d
(1)
3D
(1)
ABG
(1)
agen JNE
(1)
almari
(1)
Alufoil
(1)
Aluminum Foil
(1)
anilox roll
(1)
apartemen
(1)
Atom
(1)
autocad
(1)
backdrop logo
(1)
bagian dalam
(1)
bangunan
(1)
batu alam
(1)
berkualitas
(1)
bermutu
(1)
berpengalaman
(1)
bertingkat
(1)
birdview
(1)
black and white
(1)
botol plastik
(1)
cafe
(1)
classic
(1)
coklat
(1)
cold rolled sheet
(1)
Computer To Plate
(1)
concepts
(1)
Consumer Understanding
(1)
control movement
(1)
counter
(1)
create
(1)
CTP
(1)
denah berwarna
(1)
denah kantor
(1)
desain
(1)
desain cuci mobil
(1)
desain kamar
(1)
desain produk
(1)
design
(2)
Design and Function
(1)
design meja
(1)
Design restaurant
(1)
design rumah
(1)
development
(1)
di daerah
(1)
dinding bata
(1)
dining
(1)
Duromer
(1)
Electrons
(1)
etnik
(1)
factors
(1)
flexo packaging
(1)
flexo printing
(1)
food
(1)
furniture
(1)
gallus
(1)
gambar
(1)
gaya modern
(1)
gloss
(1)
grc kotak
(1)
Halftone
(1)
hanya 550 ribu
(1)
harga murah
(1)
hasil cepat
(1)
hotel
(1)
industrial
(1)
injection
(1)
Injection Mold
(1)
ink
(1)
inovatif
(1)
install
(1)
interior
(1)
interior rumah
(1)
jasa gambar rumah
(1)
jasa 3d
(1)
jasa arsitek
(1)
jasa desain
(1)
jasa desain 3d
(1)
jasa design
(1)
jasa designer
(1)
jasa gambar
(1)
kamar tidur
(1)
kamar tidur anak
(1)
kampus
(1)
karaoke
(1)
kawasan
(1)
kawasan industri
(1)
kemasan
(1)
kerja di rumah
(1)
kitchen set
(1)
kontemporer
(1)
kosan
(1)
kost
(1)
krem
(1)
laci
(1)
lamination
(1)
lithography
(1)
living room
(1)
livingroom
(1)
lounge
(1)
Luscher MultiDX
(1)
masterplan
(1)
matt
(1)
meja kerja
(1)
metalworking
(1)
mewah
(1)
minimalis
(1)
minimalist
(1)
modern
(1)
mold
(1)
molding
(1)
Monomer
(1)
murah
(1)
murah.
(1)
Neutron
(1)
nuansa remaja
(1)
offset
(1)
online design
(1)
open ceiling
(1)
outdoor
(1)
overprint
(1)
pabrik
(1)
pantai
(1)
pencahayaan
(1)
perumahan
(1)
pesan desain
(1)
pesan desain toko
(1)
plastic
(1)
plug
(1)
Polimer
(1)
Polyaddition
(1)
Polycondensation
(1)
Polymerization
(1)
Polystyrene
(1)
printing ink
(1)
product
(1)
Product Creation
(1)
product design
(1)
product function
(1)
produk katalog
(1)
Protons
(1)
prototype
(1)
Raster Image Processor
(1)
register
(1)
rendering
(1)
research
(1)
resepsionis
(1)
responsibility
(1)
resto industrial
(1)
RIP
(1)
Rotary
(1)
ruang kantor
(1)
ruang keluarga
(1)
ruang kerja
(1)
ruang tamu
(1)
ruang tunggu
(1)
ruko
(1)
rumah
(1)
rumah hook
(1)
rumah susun
(1)
rumah tropis
(1)
scandinavian
(1)
screen printing
(1)
sederhana
(1)
sempoa
(1)
setup
(1)
simple sederhana
(1)
specifications
(1)
spring
(1)
steel
(1)
Struktur Plastik
(1)
suspension
(1)
sweet home
(1)
taman
(1)
tampak
(1)
tampak rumah
(1)
Technological Change
(1)
terbaru
(1)
termurah
(1)
toko aksesoris
(1)
toko asesoris
(1)
trapping
(1)
two cavity
(1)
unscrewing
(1)
use
(1)
uv varnish
(1)
via online
(1)
website
(1)